Beautiful Work Info About Provision For Bad Debts

Bad debts are possible whenever credit is extended to customers.
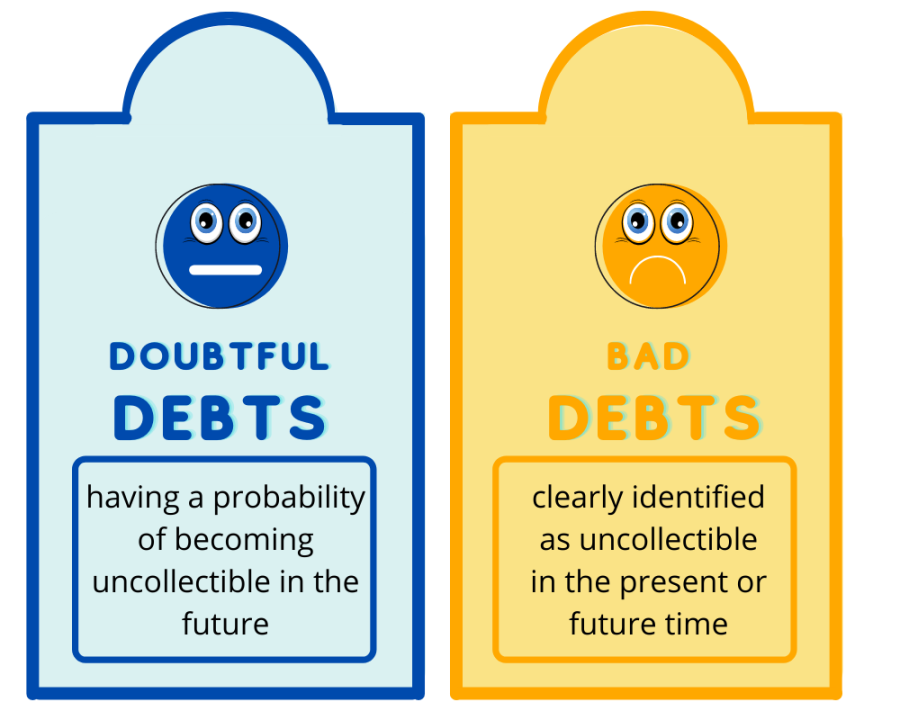
Provision for bad debts. The provision for doubtful debts is the estimated amount of bad debt that will arise from accounts receivable that have been issued but not yet collected. Below is an example of a bad debt provision. Provision for bad debts the provision for bad debts is not the same as bad debts.
The term “bad debt provision” refers to creating an asset account that reflects credit balance, which, coupled with the accounts receivable, captures the net realizable value of the company’s debtors. There are several ways to make the estimates, called provisions , some of which are legally required while others are strategically preferred. If a creditor has a bad debt on the books, it becomes uncollectible and is recorded as a.
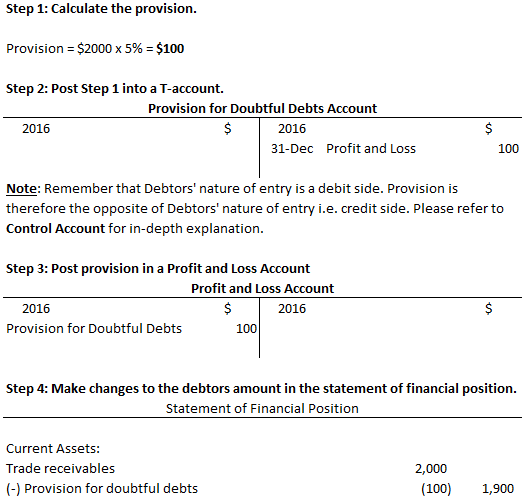
We record this future loss of debts as soon as we are aware that we will definitely lose money in the future. That is, the management may apply say 2% to all receivables from 30 to 60 days, 10% to all receivables from 61 to 180 days and 100% to all receivables with an ageing of more than 180 days. Recommended articles key takeaways bad debt refers to the extended credit that businesses offer customers, which they fail to repay within the promised tenure.
A bad debt is a receivable that a customer will not pay. It is similar to the allowance for doubtful accounts. Provisions are measured at the best estimate (including risks and uncertainties.
The provision for the bad debt is an expense for the business and a charge is made to the income statements through the bad debt expense account. Therefore, the entrepreneur need to create a provision to safeguard his financial reports. This is also referred to.
But the accountant is unsure when or how much the loss/expenses may occur. The provision for doubtful debts is an estimated amount of bad debts that are likely to arise from the accounts receivable that have been given but not yet collected from the debtors. Overview, calculate, and journal entries.
A provision for bad debts is the probable loss or expenses of the immediate future. A provision calculated to cover the debts during an accounting period that are not expected to be paid. The provision for bad debts could refer to the balance sheet account also known as the allowance for bad debts, allowance for doubtful accounts, or allowance for uncollectible accounts.
A provision for bad debts is the different from the bad debts where the loss or expenses is certain. The rationale of providing for bad debt is because we doubt a certain percentage of the sundry (total) debtors may fail to pay. Any company that has a policy of selling goods on credit has to deal with the problem of bad debts.
They arise when a company extends too much credit to a customer that is incapable of paying back the debt, resulting in either a delayed, reduced, or missing payment. By correctly accounting for bad debts, businesses can ensure that their accounts are accurate and compliant with the relevant regulations. Bad debt is an amount of money that a creditor must write off if a borrower defaults on the loans.
The balance in this account does not belong to any specific debtor or creditors but is held as general provisions. Apply certain percentage of provision to each ageing group of receivables based on management estimates. It adversely affects any business organization being identified as an unforeseen loss of working capital.