Looking Good Tips About Bad Debt Expense Financial Statement

Recording uncollectible debts will help keep your books balanced and give you a more accurate view of your accounts receivable balance, net income, and cash flow.
Bad debt expense financial statement. A bad debt expense is a financial transaction that you record in your books to account for any bad debts your business has given up on collecting. It involves determining the amounts that cannot be collected from consumers and appropriately reflecting them on the balance sheet. Recognizing bad debts leads to an offsetting reduction to.
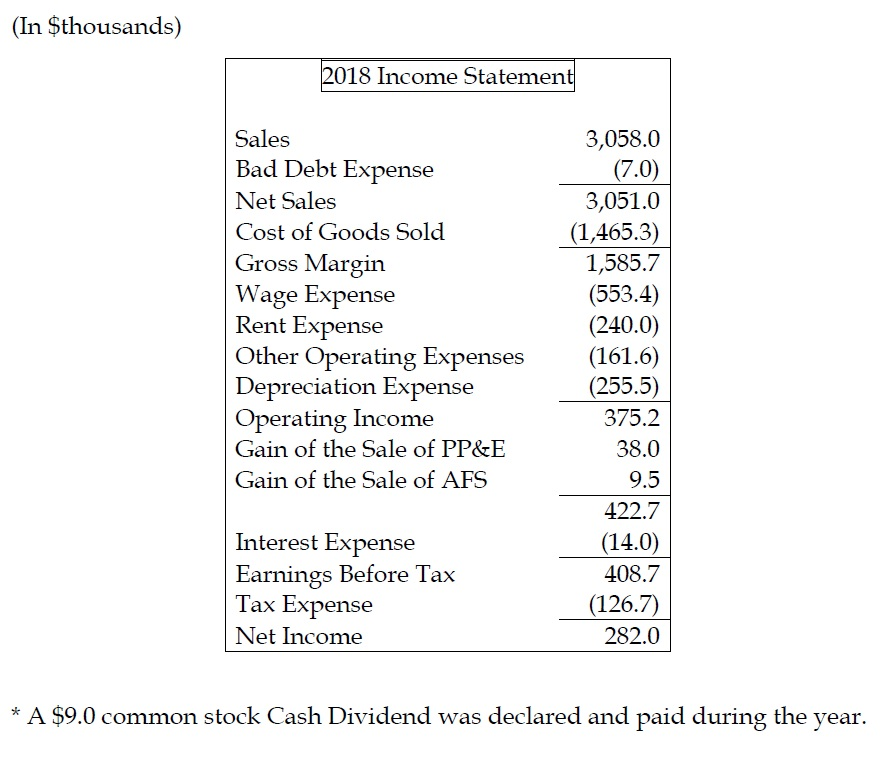
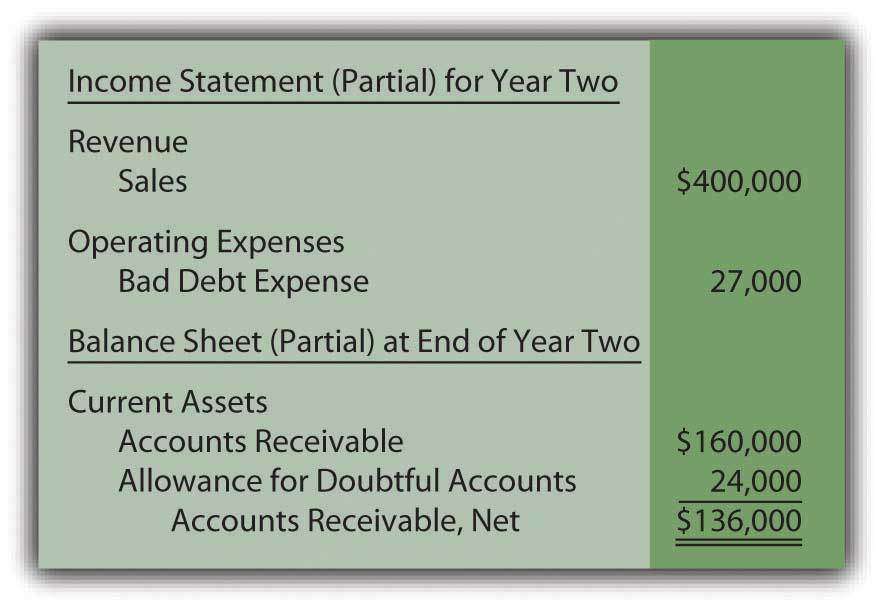
Bad debt expense is an expense recorded in financial statements when amount receivable from debtors are not recoverable due to inability of debtors to meet their financial obligation and can be calculated using direct allowance/estimation method. These are mainly the administrative, selling and distribution expenses. On the income statement, the bad debt expense is recorded in the current period to abide by the matching principle, while the accounts receivable line item on the balance sheet is reduced by the allowance for doubtful accounts.
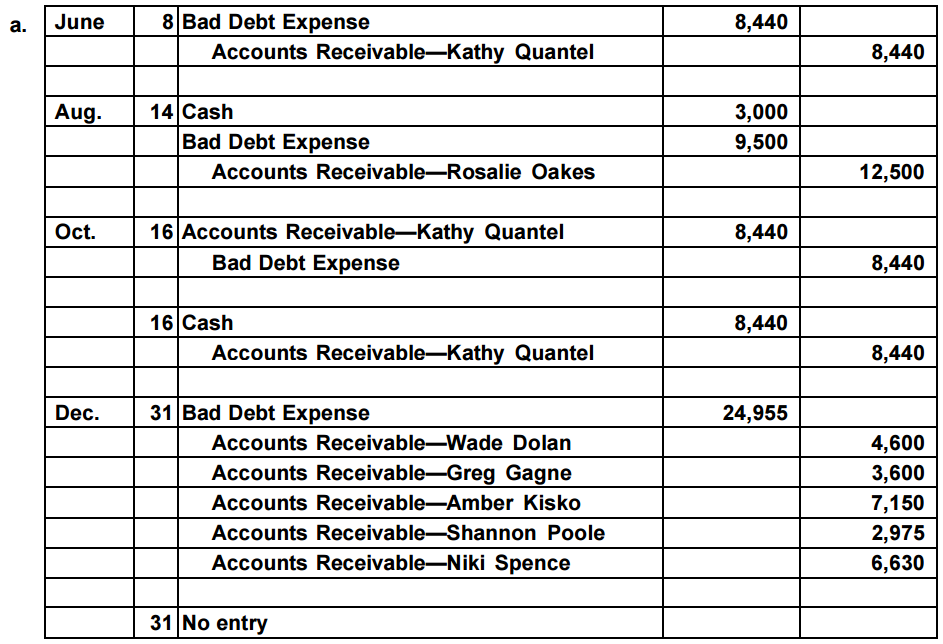
The journal entry for our hypothetical scenario is as follows. The journal entry for bad debt expense is a crucial accounting process that ensures accurate financial reporting and a strong financial position for a company. Michael barr, who oversees bank supervision at the us.
Reporting bad debt expense on income statement allows companies to accurately and completely report their financial position. Bad debt expenses are usually categorized as operational costs and are found on a company’s income statement. Accounting for a credit or loan agreement can be distilled into four key steps:
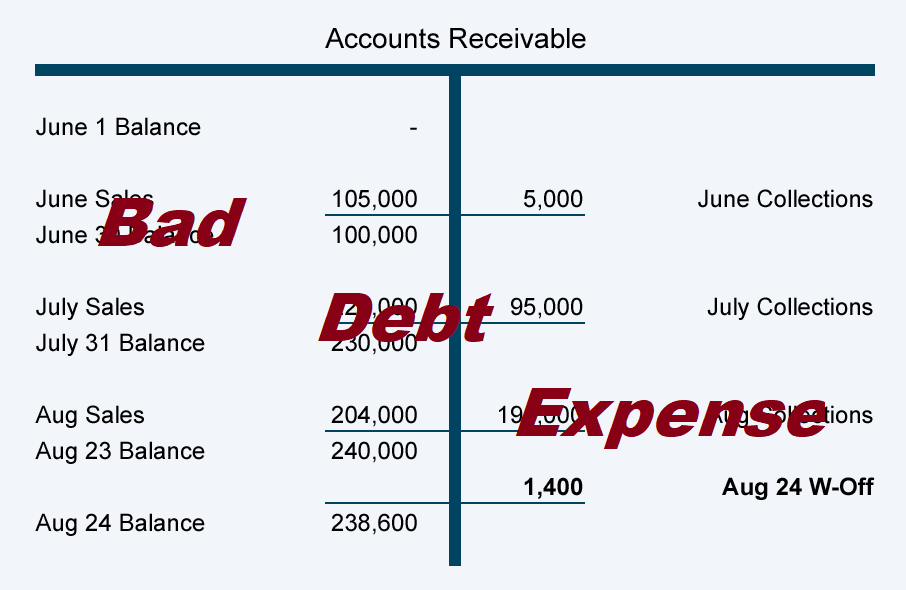
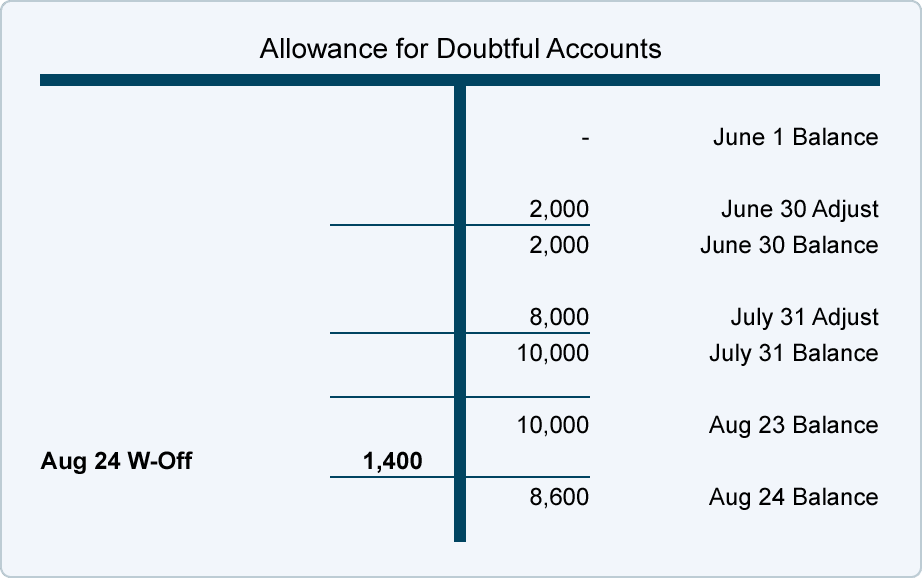
If the actual bad debt was greater than the provision, the bad debt expense must be tracked on the income statement for the same accounting period during which the loan or credits were issued. On the balance sheet, bad debt is recorded as a reduction in the accounts receivable asset account. For example, in one accounting period, a company can experience large increases in their receivables account.
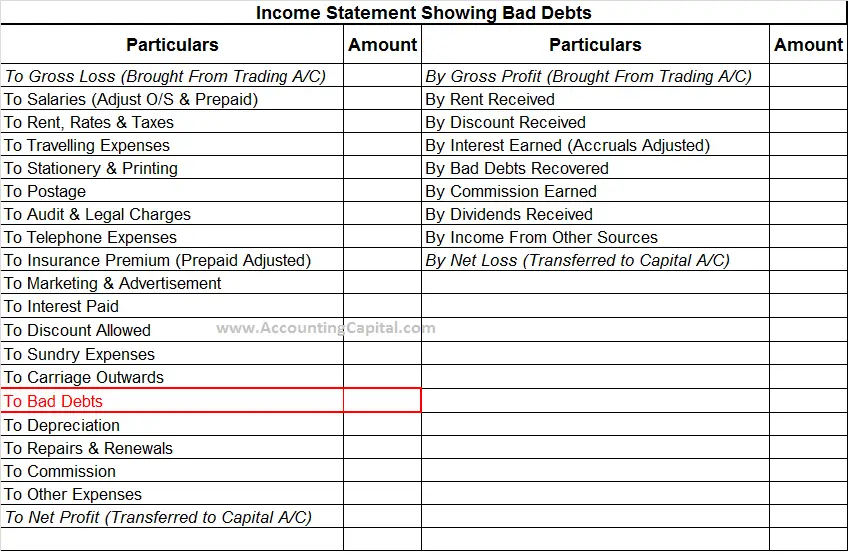
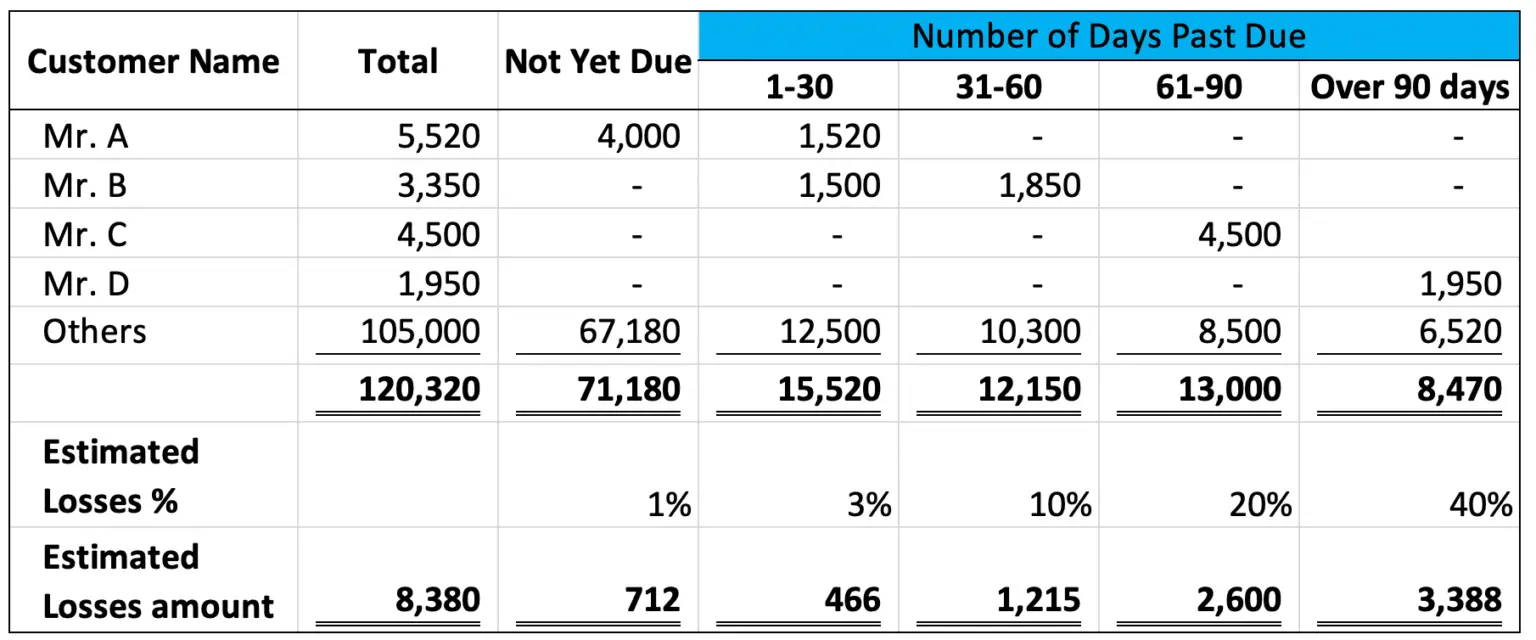
The company usually calculate bad debt expense by using the allowance method. Companies must account for bad debt expenses in their financial statements to comply with generally accepted accounting principles (gaap). With respect to financial statements, the seller should report its estimated credit losses as soon as possible using the allowance method.
The allowance method is to estimate the amount of bad debt by deducting receivables related allowances from total accounts receivable. Bad debt expense is a significant component in financial statements as it addresses uncollectible debts. This can have a negative impact on the company's profitability and may cause its earnings per share to decrease.
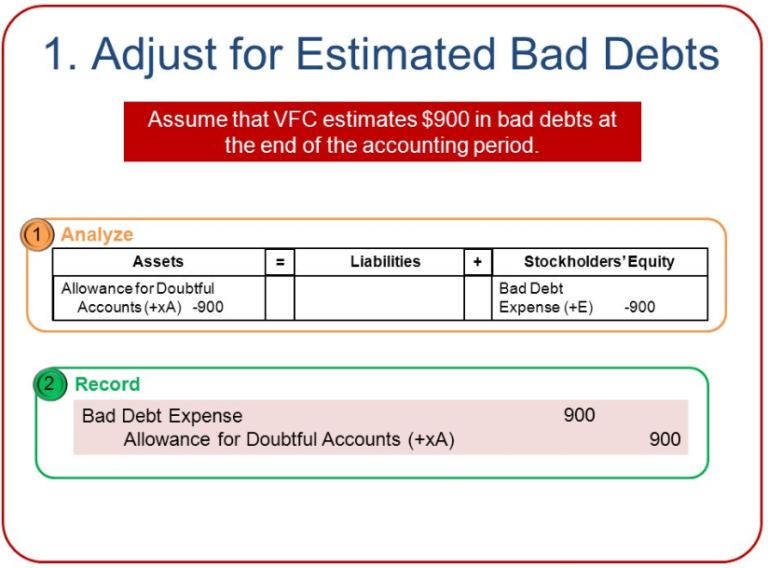
The income statement records bad debt as an expense and reduces the company's net income. A credit loss or bad debts expense on its income statement, and a reduction of accounts receivable on its balance sheet. Bad debt expense increases (debit) as does allowance for doubtful accounts (credit) for $58,097.
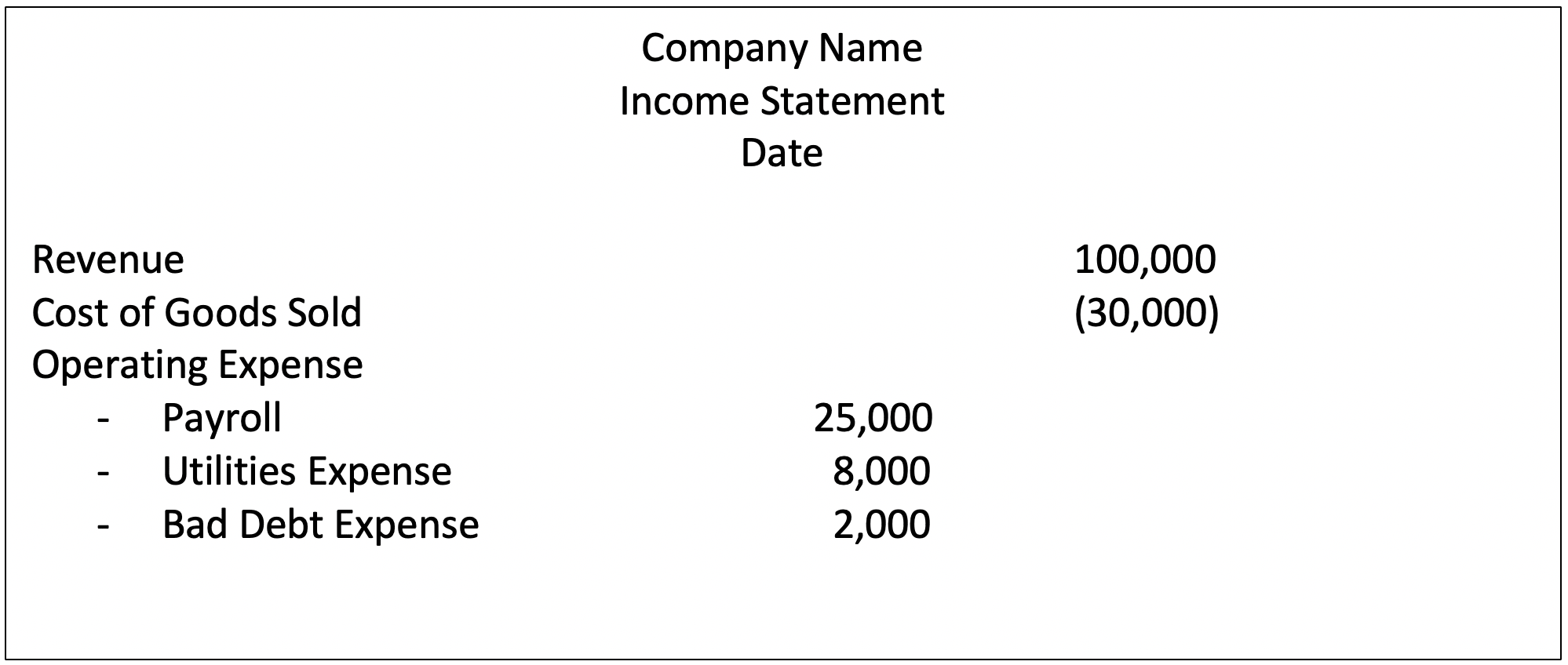
All expenses which are not directly related to the main business activity will be reflected in the profit & loss a/c. A bad debt expense is a financial transaction that your business records in its books to account for any bad debts it has given up trying to collect. Bad debt expense is the loss that incurs from the uncollectible accounts, in which the company made the sale on credit but the customers didn’t pay the overdue debt.
Though part of an entry for bad debt expense resides on the balance sheet, bad debt expense is posted to the income statement. You only have to record bad debt expenses if you use accrual accounting principles. This method requires that a company evaluate the percentage of customers that will not pay for their order and then calculate the allowance for these debts.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/AmazonBS-33b2e9c06fff4e63983e63ae9243141c.JPG)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/BadDebtExpense-resized-ebb42a883975499490c801c7bfc35355.jpg)
![Here's How to Calculate Bad Debt Expense [FORMULA EXPLAINED]](https://passiveincometoretire.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/how-to-calculate-bad-debt-expense.jpg)